Skin diseases are a class of ailments that affect the human skin which represents the largest organ of the human body.
Skin is the largest organ in the body and it is the most important organ for it provides protection against diseases causing agents and extremes of temperature besides being involved in sensation.
Nonetheless, influences like heredity, toxic substances, diet and other lifestyles, and illnesses can cause skin diseases from simple, short-lived to complicated and long-standing.
All over the world, skin diseases have become among the most prevalent diseases that affect humans across all ages.
The symptoms include but are not limited to acne, eczema, psoriasis, general infections which not only affect a person’s appearance, but also their overall well-being, normal functioning, mood, and self-esteem.
It is important to learn about skin diseases, the causes, symptoms, and ways to treat or prevent skin diseases that benefit the promotion of skin health.
This article aims to deepen understanding of skin diseases, discuss their types and causes, their signs and symptoms, measures in helping to solve them, highlighting the significance of diagnostically early detection and timely treatment to maintain skin health.
What are the types of skin diseases?

Skin diseases refer to diseases in which the skin, nails or hair are targets of the disease. These can be grouped according to their cause, character or sign. Below are the primary types of skin diseases:
Common Skin Diseases
Acne:
- Interacts with the hair and sebaceous gland.
- Being mostly featured by pimples, black heads and white heads.
Eczema:
- It consists of atopic and contact dermatitis.
- Some of the signs are skin rash which is red, skin itching and skin inflammation.
Psoriasis:
- Type of autoimmune disease that manifests characterized by symptoms of thick skin often with scales.
Rosacea:
- When it is severe, such can cause redness, flushing, and what may resemble circulation on the face.
Infectious Skin Diseases
Bacterial Infections:
- Examples: Impetigo, cellulitis.
- Commonly developed due to Staphylococcus or Streptococcus germs.
Viral Infections:
- Examples: Warts (caused by HPV), herpes simplex or cold sores.
Fungal Infections:
- Examples: Ringworm, athlete’s foot, candidiasis.
- May be provoked by fungi such as Candida or Dermatophytes.
Parasitic Infections:
- Examples: Scabies, which is caused by mite lice.
Allergic Skin Diseases
Hives (Urticaria):
- Some of these conditions are caused by allergens and present themselves as red, itchy skin lesions that form raised welts.
Contact Dermatitis:
- Which occurs due to skin touch with a problematic substance like the poison ivy or exposure to chemicals.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory skin diseases
Vitiligo:
- Rubia alba: That’s a condition whereby melanocytes cells that produce skin pigments are destroyed by the body’s own immune system leading to absence of skin color.
Lupus:
- May lead to a butterfly Rash on the face plus other manifestations on the skin.
Scleroderma:
- Sagging or things seem tighter which is caused by increased collagen.
Skin Cancer and its Precursor Lesions
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
- An ordinary type of a cancer that affects the skin and is generally slow growing.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
- Develops in the dermis and may be malignant.
Melanoma:
- The worst type of skin cancer, which starts in the melanin producing cells.
Genetic Skin Diseases
Ichthyosis:
- A category of diseases that result in skin conditions that are’; Silky and rough.
Albinism:
- Hereditary disorder marked by decreased level of melanin in skin, hair and iris.
Occupational Skin Diseases
Occupational Dermatitis:
- Pulmonary diseases develop as a result of coming into contact with chemicals or other hazardous substances in the workplace.
Hand Eczema:
- Including regular users of chemicals or toxic products in the course of their working activities.
Pigmentation Disorders
Hyperpigmentation:
- Lesions that can be attributed to pigmentary disorder; hyperpigmented skin.
Hypopigmentation:
- In other cases, hypopigmentation results in lighter colors of skin than usual, or the skin may be wholly or partially lacking color or blush.
Other Skin Conditions
Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- It causes dandruff and scaly skin especially along the scalp.
Keratosis Pilaris:
- Knot like, raised skin disks usually found on the arms and thighs.
Alopecia Areata:
- A type of autoimmune disorder that leads to alopecia in patches.
These skin diseases might also be characterized by different causative agents, signs and management. Professional help should be sought to obtain a correct diagnosis and to control the disease.
Read more: تعليمات ما بعد حقن البوتوكس: أهمية الرعاية لنتائج أطول
Causes and Risk Factors of Skin Diseases
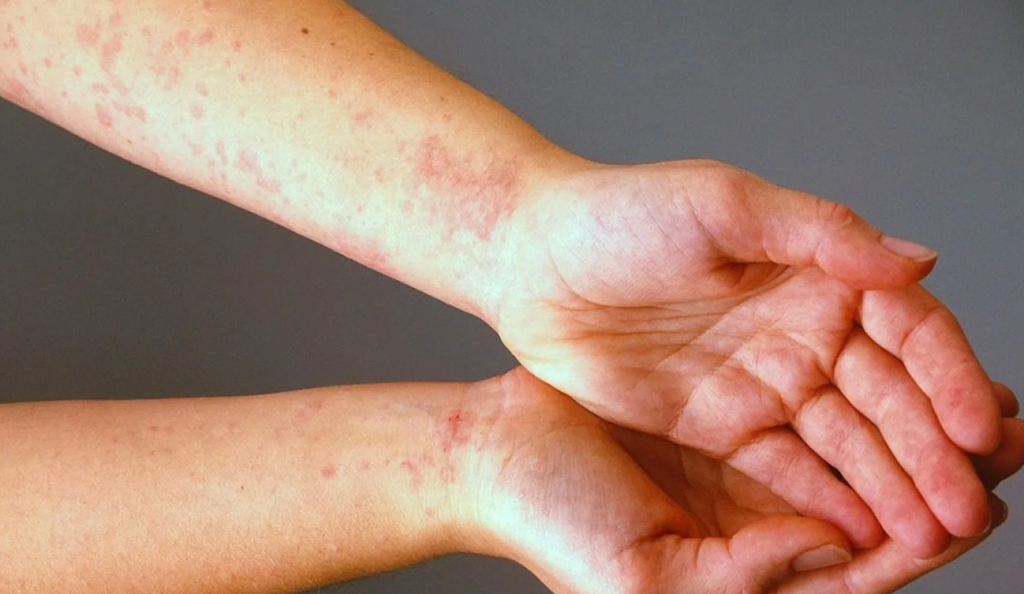
Skin diseases are caused by external and internal factors. Knowledge of these causes and risk factors may help prevent the condition, make earlier diagnoses or treatment, and prevent complications.
Genetic Factors
Family History:
- The four conditions including eczema, psoriasis, and vitiligo primarily have genetic factors.
Inherited Disorders:
- Disorders such as albinism or ichthyosis carry genetic mutations inherited over the years.
Environmental Factors
Allergens:
- Some of the causes of skin allergy that may be caused by substances such as pollen, dust, foods such as wheat, or cosmetics.
Pollutants:
- Hazards in the air can cause skin irritation and worsen such skin disorders as eczema or acne.
Climate and Weather:
- These conditions such as extreme temperatures, high humidity and strong sun rays can have a negative impact on skin and can lead to dangerous diseases.
Lifestyle Factors
Hygiene Practices:
- Bad hygiene makes development of bacterial or fungal infection possible.
- Using water excess or a chemical product with high abrasiveness can cause problems to the skin barrier.
Diet and Nutrition:
- Lack of nutrients (vitamin C, zinc and others) cause poor skin health and skin failure.
- There are ways in which diet influences acne through, high glycemic index foods lead to acne flare up.
Stress:
- It is common knowledge that stress can cause psoriasis, can hinder the improvement process in eczema or worsen acne.
Medical and Health Conditions
Immune System Disorders:
- Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus or scleroderma rash have symptoms on skin .
Hormonal Changes:
- Skin changes related to puberty, pregnancy, or menopause may cause acne or melasma.
Infections:
- Predominantly, skin diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. Some excellent examples of a contagious skin condition are warts which are caused by the Human Papillomavirus, bacterial impetigo, and scabies that result from mite infestation.
Chronic Conditions:
- Diabetes can cause a slower rate of healing of wounds and can result in such infections like skin.
- Diabetes can cause decelerated porosity of healing in wounds and skin.
Work-Related and LifeStyle Factors
Chemical Exposure:
- Some professions react with the irritants or allergens and hence produce contact dermatitis.
Excessive Sun Exposure:
- People are able to also raise chances of sunburn, skin aging, and more sensitive kinds of skin cancer such as melanoma.
Aging and Skin Changes
Aging Process:
- The skin loses elasticity, keratinization, and becomes more susceptible to conditions as eczema or pressure ulcers.
Loss of Collagen:
- Causes fine lines and creases, and makes skin more vulnerable to harm.
Psychological Factors
Mental Health:
- Stress and anxiety make it worse for skin conditions such as eczema, rosacea and psoriasis.
Behavioral Habits:
- Skin-picking disorders, which are usually associated with anxiety, can lead to scar or infection.
The prevention and detailed control of these causes and risk factors need a systematic one, healthy practices, necessary medical documentation, and consulting with the doctor when suitable.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Skin Diseases

As with most skin diseases, knowledge of symptoms and the diagnosing process is very important for a timely treatment. There are many types of skin diseases and proper diagnosis will form the basis of proper treatment.
Symptoms of Skin Diseases
1. General Symptoms
Rashes:
- Dermatophyte lesions which are red, Inflamed and can be to varying size and may be flat or raised.
- Examples: Eczema, allergic reactions.
Itching (Pruritus):
- Scratching is classified as persistent or intermittent tended with dryness or inflammation of the skin.
- Examples: Psoriasis, scabies.
Discoloration:
- Discolored skin, including dark or light skin areas (e.g., vitiligo, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation).
Scaling or Peeling:
- Had scaly and dry skin or skin that was shedding because of bacterial or fungal infections.
- Examples: Psoriasis, athlete’s foot.
Blisters:
- Blisters formed as a result of friction, burns, or infections filled with fluids.
- Examples: Herpes simplex, impetigo.
Bumps or Growths:
- Tumors, growths or nodules which may be non cancerous or cancerous.
2. Specific symptoms
- Psoriasis: White scales reflecting situ and thickened plaques and arthritic manifestations in some individuals.
- Eczema: This is characterized by skin redness, itching, and cracking which is made worse by exposure to an allergen.
- Rosacea: Redness of the face, telangiectasias, and response to causative factors like light or spicy foods.
- Fungal Infections: Rash that forms a circle around the limb or trunk with itching or burning sensation.
- Skin Cancer: Abnormal or developing moles with asymmetrical edges, odd colours or faster than expected rates of growth.
3. Signs of Systemic Disorders
- Fever and Fatigue: May present with bacterial, viral or fungal infections or autoimmune skin diseases.
- Pain or Tenderness: Frequent in disease like cellulitis or herpes zoster Otherwise referred to as shingles.
Diagnosis of Skin Diseases
1. Medical History
Patient Interview:
- Speaking and understanding on when the symptoms started, last, and the factors that ignite it.
- Questions about skin diseases or allergic diseases in members of the patient’s family.
Lifestyle Assessment:
- Data regarding previous workplace exposures or skin care regimen or recent travel history.
2. Physical Examination
Visual Inspection:
- Evaluating shape, status location and distribution of the lesions or changes.
Touch Examination:
- Touching the skin to feel for lesions, hardness in swellings additionally checking the temperature of affected parts of the body.
3. Diagnostic Tests
Skin Biopsy:
- Surgical excision of a skin lesion for histopathological examination.
- Doctors employ them while diagnosing cancers, Autoimmune diseases, or any other unusual rash.
Patch Testing:
- Establishing the cause of contact dermatitis The signs and symptoms Expert opinion Location History Diagnosis of the condition Allergens at the workplace Allergens at home Demographics Frequency Food triggers Travel exposure New allergens Cause of flare-ups Duration of flare-ups.
Blood Tests:
- Identifying hidden chronic disorders like lupus, infections.
Microscopic Examination:
- Biopsy of the skin lesions to find fungi, bacteria or parasites growing in the affected skin.
Wood’s Lamp Test:
- Some other brilliant applications may be as a diagnostic tool when diagnosing fungal diseases, or diseases related to pigment production.
4. Special emphasis and imaging
Dermatoscopy:
- Screening skin moles or lesions by imaging techniques without having to perform a biopsy to determine whether the growth is melanoma.
Molecular Testing:
- Looking for disease-associated genes in autosomal dominant skin diseases.
Anyone who experiences changes in the skin color or texture that are persistent or strange should seek a dermatologist’s attention earlier enough to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Read more: جلسة الديرمابن: ما هي فوائدها وكيف تجعل بشرتك أكثر نضارة؟
Treatment and Management of Skin Diseases
Skin diseases can be treated and managed on the basis of cause, severity and the type of skin ailment present in the patient.
The management of these diseases by dermatologists involves drug Prescription, lifestyle changes and preventive measures.
1. Medical Treatments
A. Topical Treatments
Corticosteroids:
- Alleviate inflammation along with itching in skin diseases such as eczema, dermatitis or even psoriasis.
Antibiotic Creams:
- Use for bacterial skin conditions such as impetigo or infection of a skin ulcer.
Antifungal Creams:
- Good for treating fungal infections which are common with such diseases like athlete’s foot or ringworm.
Retinoids:
- That is useful in conditions such as acne, psoriasis and photoaging as it stimulates skin cell shedding.
Moisturizers and Emollients:
- Supply skin with water and rebuild skin’s barrier function especially where skin is dry due to certain skin diseases or old age.
B. Oral Medications
Antibiotics:
- This is used for treating potentially severe bacterial infections as well as acne.
Antifungal Pills:
- Prescribed for severe and deep-seated or chronic mycoses.
Antiviral Drugs:
- Manage herpes simplex or shingles for example with acyclovir.
Immunosuppressants:
- Treat autoimmune diseases – for instance, lupus or severe eczema.
Antihistamines:
- Treat itching and allergic symptoms, including but not limited to, rash, eczema, and hives.
C. Advanced Therapies
Biologic Drugs:
- Prefer some areas of the immune system for things like psoriasis or eczema.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
- It uses UV light to alleviate signs of psoriasis, eczema or vitiligo.
Cryotherapy:
- Freezing and taking out of skin growth that are considered unusual such as warts or precancerous tissues.
2. Surgical Interventions
Excision:
- Surgically excising skin tumors – skin cancers, cysts or any other aberrant tissues.
Laser Surgery:
- Can be used in management of scar, skin discoloration or vascular disorders such as rosacea.
Dermabrasion and Chemical Peels:
- Fine lines, wrinkles, and sun damage, skin discoloration and ageing, and scar tissue can thus be rejuvenated.
3. Natural Cures and Herbal Cure
Aloe Vera:
- It Fights inflammation and also works as an anti healing agent.
Oatmeal Baths:
- Ease inflammation in circumstances such as dermatitis, or chicken pox.
Tea Tree Oil:
- Antibacterial and antifungal effects for mild acne or infections.
Coconut Oil:
- Used in management of dry or irritated skin.
4. Lifestyle changes
Skincare Routine:
- Select mild, non drying goods that do not cause delicate facial skin irritation.
- Use sunscreen every day to avoid skin injury caused by ultraviolet radiation.
Diet and Hydration:
- Take foods with a lot of vitamins and antioxidants – Vitamin C & zinc, for instance.
- Drink enough water so as to enhance the skin hydration.
Avoid Triggers:
- Avoid exposure to such allergens, chemicals or stress factors in order to prevent their accidental exposure.
Maintain Hygiene:
- Cleaning of the skin continually to avoid such infections.
Positive changes in outcomes of patients with skin diseases can be achieved by integrated medical, behavioral interventions and psychosocial management. There is no one size fits all formula; consulting a dermatologist for a personalized plan is the next step.
Prevention of Skin Diseases
It is crucial to point out that skin diseases prevention requires responsible behavior, skin’s protection against damaging factors and certain changes in one’s life. Though some conditions may be hereditary or perhaps unavoidable, a large percentage are manageable through adequate supervision.
1. Maintain Proper Hygiene
Regular Cleansing:
- Cleaning the skin twice daily with mild, non-abrasive products helps to cleanse the skin surface of dirt, oil and bacteria.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items:
- This is in judgment from sharing towels, razors, and cosmetics that spread infectious diseases such as fungal diseases or bacteria that cause acne.
2. Protect the Skin from the Sun
Use Sunscreen:
- Use a wide spectrum sunscreen lotion (SPF 30 or more) daily to protect yourself from future UV damage.
Wear Protective Clothing:
- Wear hats, full-sleeved clothes and sunglasses when you are out in the sun.
Avoid Tanning Beds:
- Tanning bed rays cause skin cancer and early aging of the skin, an efficient way to kill oneself.
3. Avoid Skin Irritants
Identify Allergens:
- One should do a patch test whenever they plan to use a new skincare, cosmetic, or makeup product.
Use Mild Products:
- Use only skin- and respiratory-irritant-free washing soap, laundry soap, and other personal care products like lotion, shampoo, and conditioner.
4. Follow a Healthy Diet
Balanced Nutrition:
- To encourage skin health you should include foods containing vitamins A, C, E and omega 3 fatty acids.
- Ensure you take a lot of water when drinking so as to help improve skin.
Avoid Trigger Foods:
- Avoid foods which are rich in sugar and fats and which can cause acne or irritation of the skin.
5. Preserve Your Hair
Gentle Cleansing:
- Do not scrub the area with vigorous pressure or use hot water because this will dispense with the skin oils.
Moisturize Regularly:
- When choosing creams to apply, ensure it is for the skin type to avoid dry skin and compromise of the skin’s barrier.
6. Prevent Infections
Treat Wounds Properly:
- Wash the wound and protect it from getting infected with some bandage.
Keep Feet Dry and Clean:
- Avoid getting a fungal infection such as athlete’s foot by putting on and wearing shoes that are permeable and socks.
In Conclusion
Skin diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that can impact both physical and emotional well-being.
While some skin disorders may be minor and easily treatable, others can be chronic or life-threatening if left unmanaged.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing complications.
Preventive measures, such as maintaining proper hygiene, protecting the skin from environmental damage, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the risk of developing many skin conditions.
Early diagnosis and timely medical intervention are vital in managing symptoms effectively and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by skin diseases.
By prioritizing skin health through awareness, care, and professional guidance, individuals can protect their skin and ensure it remains a resilient barrier against external challenges, reflecting overall well-being.
